Expert Systems in AI
What is an Expert System?
An expert system is a computer program that is designed to solve complex problems and to provide decision-making ability like a human expert. It performs this by extracting knowledge from its knowledge base using the reasoning and inference rules according to the user queries.
The expert system is a part of AI, and the first ES was developed in the year 1970, which was the first successful approach of artificial intelligence. It solves the most complex issue as an expert by extracting the knowledge stored in its knowledge base. The system helps in decision making for complex problems using both facts and heuristics like a human expert. It is called so because it contains the expert knowledge of a specific domain and can solve any complex problem of that particular domain. These systems are designed for a specific domain, such as medicine, science, etc.
The performance of an expert system is based on the expert's knowledge stored in its knowledge base. The more knowledge stored in the KB, the more that system improves its performance. One of the common examples of an ES is a suggestion of spelling errors while typing in the Google search box.
Below are some popular examples of the Expert System:
- DENDRAL: It was an artificial intelligence project that was made as a chemical analysis expert system. It was used in organic chemistry to detect unknown organic molecules with the help of their mass spectra and knowledge base of chemistry.
- MYCIN: It was one of the earliest backward chaining expert systems that was designed to find the bacteria causing infections like bacteraemia and meningitis. It was also used for the recommendation of antibiotics and the diagnosis of blood clotting diseases.
- PXDES: It is an expert system that is used to determine the type and level of lung cancer. To determine the disease, it takes a picture from the upper body, which looks like the shadow. This shadow identifies the type and degree of harm.
- CaDeT: The CaDet expert system is a diagnostic support system that can detect cancer at early stages.
Characteristics of Expert System
- High Performance: The expert system provides high performance for solving any type of complex problem of a specific domain with high efficiency and accuracy.
- Understandable: It responds in a way that can be easily understandable by the user. It can take input in human language and provides the output in the same way.
- Reliable: It is much reliable for generating an efficient and accurate output.
- Highly responsive: ES provides the result for any complex query within a very short period of time.
Components of Expert System
An expert system mainly consists of three components:
- User Interface
- Inference Engine
- Knowledge Base
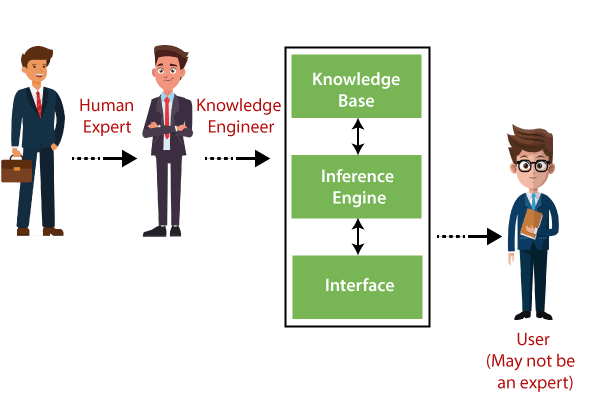
1. User Interface
With the help of a user interface, the expert system interacts with the user, takes queries as an input in a readable format, and passes it to the inference engine. After getting the response from the inference engine, it displays the output to the user. In other words, it is an interface that helps a non-expert user to communicate with the expert system to find a solution.
2. Inference Engine(Rules of Engine)
- The inference engine is known as the brain of the expert system as it is the main processing unit of the system. It applies inference rules to the knowledge base to derive a conclusion or deduce new information. It helps in deriving an error-free solution of queries asked by the user.
- With the help of an inference engine, the system extracts the knowledge from the knowledge base.
- There are two types of inference engine:
- Deterministic Inference engine: The conclusions drawn from this type of inference engine are assumed to be true. It is based on facts and rules.
- Probabilistic Inference engine: This type of inference engine contains uncertainty in conclusions, and based on the probability.
Inference engine uses the below modes to derive the solutions:
- Forward Chaining: It starts from the known facts and rules, and applies the inference rules to add their conclusion to the known facts.
- Backward Chaining: It is a backward reasoning method that starts from the goal and works backward to prove the known facts.
3. Knowledge Base
- The knowledgebase is a type of storage that stores knowledge acquired from the different experts of the particular domain. It is considered as big storage of knowledge. The more the knowledge base, the more precise will be the Expert System.
- It is similar to a database that contains information and rules of a particular domain or subject.
- One can also view the knowledge base as collections of objects and their attributes. Such as a Lion is an object and its attributes are it is a mammal, it is not a domestic animal, etc
Components of Knowledge Base
- Factual Knowledge: The knowledge which is based on facts and accepted by knowledge engineers comes under factual knowledge.
- Heuristic Knowledge: This knowledge is based on practice, the ability to guess, evaluation, and experiences.
Knowledge Representation: It is used to formalize the knowledge stored in the knowledge base using the If-else rules.
Knowledge Acquisitions: It is the process of extracting, organizing, and structuring the domain knowledge, specifying the rules to acquire the knowledge from various experts, and store that knowledge into the knowledge base
Comments
Post a Comment